Unveiling The Secrets Of Chromosome Movement In Cell Division
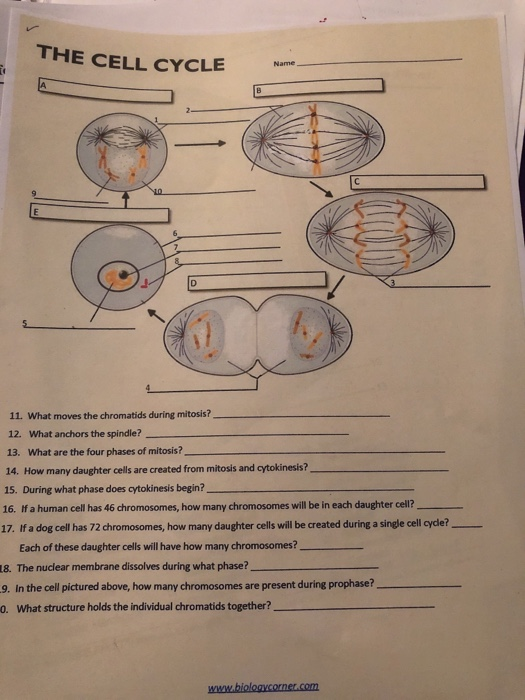
During cell division, structures called microtubules form a spindle apparatus that moves chromatids, the condensed forms of chromosomes, to opposite poles of the cell. The spindle apparatus is anchored to the centrosomes, organelles that are located near the nucleus. Centrosomes play a crucial role in organizing the spindle apparatus and ensuring the accurate segregation of chromosomes during cell division.
The proper segregation of chromosomes is essential for the survival of a cell. If chromosomes are not separated correctly, it can lead to genetic disorders and other problems. Centrosomes are essential for ensuring that chromosomes are properly separated during cell division.
Centrosomes are also involved in other important cellular processes, such as cell migration and differentiation. They are essential for the proper functioning of cells and play a vital role in the development and maintenance of tissues and organs.
Read also:Cheetah Club Sarasota Florida
Chromatid Movement and Anchorage During Cell Division
During cell division, chromatids, the condensed forms of chromosomes, are moved to opposite poles of the cell.
- Microtubules: Form the spindle apparatus that moves chromatids.
- Centrosomes: Anchor the spindle apparatus and ensure accurate chromosome segregation.
- Kinesin: Motor protein that moves chromosomes along microtubules.
- Cohesin: Protein complex that holds sister chromatids together until anaphase.
- Telomeres: Protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that prevent fusion and degradation.
- Centromere: Region of the chromosome where spindle fibers attach.
- Kinetochore: Protein complex that assembles at the centromere and binds to spindle fibers.
- Chromosome condensation: Essential for proper chromosome movement and segregation.
These aspects are all essential for the accurate segregation of chromosomes during cell division. Errors in chromosome segregation can lead to genetic disorders and other problems. Therefore, the proper functioning of these aspects is critical for the survival and development of organisms.
Microtubules
Microtubules are essential for chromosome movement during cell division. They form the spindle apparatus, a bipolar structure that attaches to the chromosomes at the kinetochore. The spindle apparatus then uses motor proteins to pull the chromosomes to opposite poles of the cell.
The accurate segregation of chromosomes during cell division is essential for the survival of a cell. If chromosomes are not separated correctly, it can lead to genetic disorders and other problems. Microtubules play a crucial role in ensuring that chromosomes are properly segregated during cell division.
In addition to their role in chromosome movement, microtubules are also involved in other important cellular processes, such as cell migration and differentiation. They are essential for the proper functioning of cells and play a vital role in the development and maintenance of tissues and organs.
Centrosomes
Centrosomes are organelles that play a critical role in cell division. They anchor the spindle apparatus, a structure made of microtubules that moves chromosomes during cell division. Centrosomes also ensure accurate chromosome segregation, which is essential for the survival of a cell.
Read also:Has Cooper Alan Won Any Awards Unveiling The Achievements Of A Rising Star
- Components of centrosomes
Centrosomes are composed of two centrioles, which are cylindrical structures made of microtubules. The centrioles are surrounded by a protein matrix called the pericentriolar material. - Role of centrosomes in spindle apparatus formation
During cell division, the centrosomes migrate to opposite poles of the cell and nucleate the formation of microtubules. These microtubules form the spindle apparatus, which is responsible for moving chromosomes during cell division. - Role of centrosomes in chromosome segregation
The centrosomes also play a role in chromosome segregation. The pericentriolar material contains proteins that bind to the kinetochores of chromosomes. The kinetochores are specialized structures on the chromosomes that attach to the spindle fibers. This attachment ensures that the chromosomes are properly segregated during cell division. - Consequences of centrosome dysfunction
Centrosome dysfunction can lead to a number of problems, including chromosome missegregation, cell division failure, and cancer.
Centrosomes are essential for accurate chromosome segregation during cell division. Their proper functioning is critical for the survival and development of organisms.
Kinesin
Kinesin is a motor protein that moves chromosomes along microtubules. It is one of the most important proteins involved in cell division. Kinesin binds to the kinetochore of a chromosome and then uses energy from ATP to move the chromosome along the microtubules of the spindle apparatus.
The movement of chromosomes by kinesin is essential for the accurate segregation of chromosomes during cell division. If kinesin is not functioning properly, chromosomes may not be properly separated, which can lead to genetic disorders such as Down syndrome.
Kinesin is also involved in other cellular processes, such as organelle transport and cell migration. It is a vital protein that plays a key role in the proper functioning of cells.
Cohesin
Cohesin is a protein complex that plays a critical role in cell division. It holds sister chromatids together until anaphase, when the chromatids are separated and pulled to opposite poles of the cell. Cohesin is essential for the accurate segregation of chromosomes during cell division.
The connection between cohesin and the movement of chromatids during cell division is as follows:
- Cohesin holds sister chromatids together until anaphase.
This prevents the chromatids from separating prematurely, which could lead to errors in chromosome segregation. - Kinesin, a motor protein, moves chromosomes along microtubules.
Kinesin binds to the kinetochore of a chromosome and then uses energy from ATP to move the chromosome along the microtubules of the spindle apparatus. - Cohesin is cleaved during anaphase.
This allows the sister chromatids to separate and be pulled to opposite poles of the cell.
The accurate segregation of chromosomes during cell division is essential for the survival and development of organisms. Cohesin plays a critical role in this process by holding sister chromatids together until anaphase.
Telomeres
Telomeres are protective caps at the ends of chromosomes that prevent fusion and degradation. They are essential for maintaining genomic stability and preventing chromosomal rearrangements. Telomeres shorten with each cell division, and when they become too short, the cell can no longer divide and enters senescence or apoptosis.
The connection between telomeres and the movement of chromatids during cell division is as follows:
- Telomeres prevent the ends of chromosomes from fusing together.
This is important because if the ends of chromosomes fuse together, it can lead to chromosomal rearrangements and genomic instability. - Telomeres help to maintain the structure of the chromosomes.
This is important because the structure of the chromosomes is essential for proper chromosome segregation during cell division. - Telomeres shorten with each cell division.
This is because the DNA polymerase enzyme that replicates DNA cannot replicate the ends of chromosomes. - When telomeres become too short, the cell can no longer divide.
This is because the cell cycle checkpoints will arrest the cell cycle if the telomeres are too short.
The maintenance of telomeres is essential for the survival and development of organisms. Telomeres protect the ends of chromosomes and help to ensure that chromosomes are properly segregated during cell division.
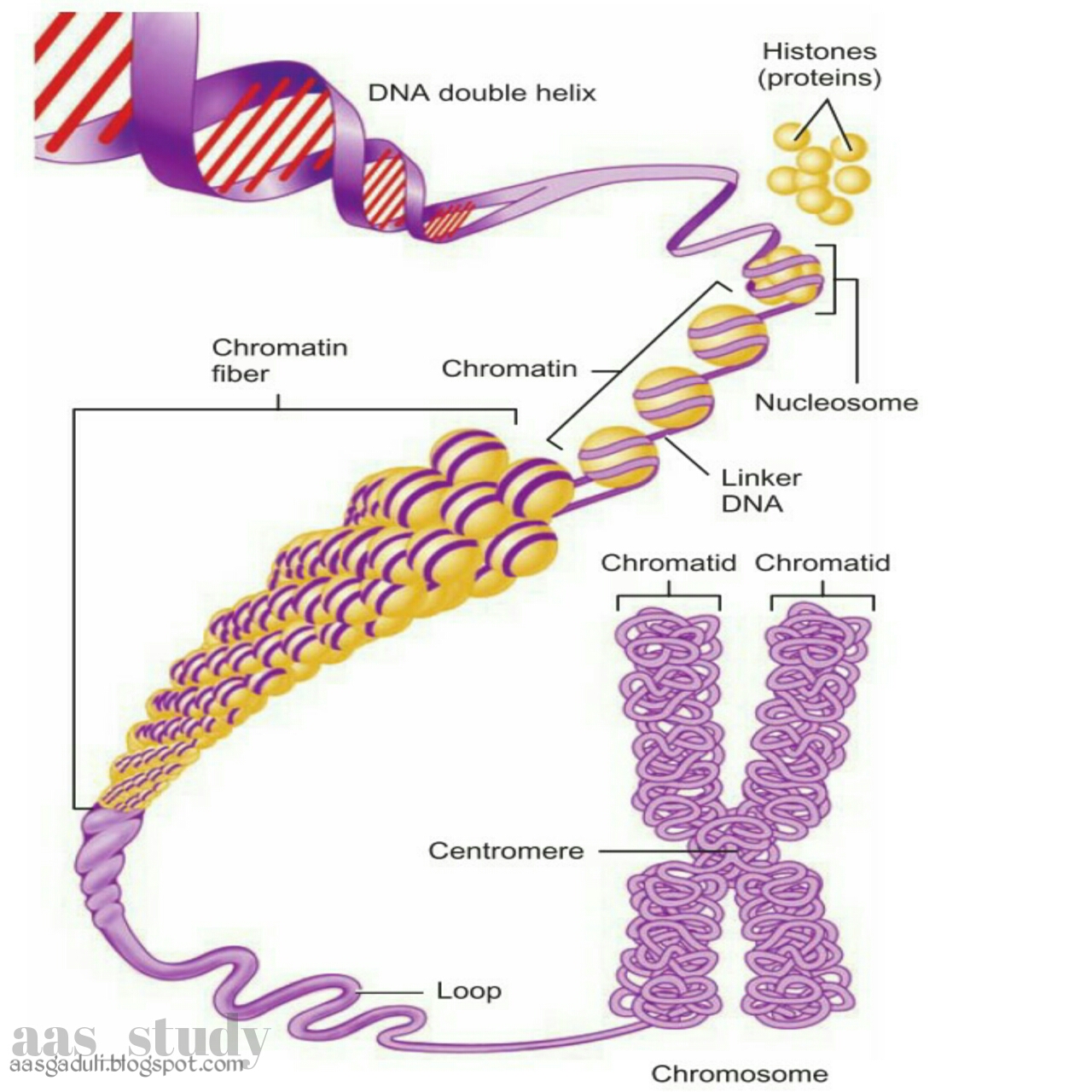
Centromere
The centromere is a specialized region of the chromosome where spindle fibers attach during cell division. It is located near the center of the chromosome and is essential for the accurate segregation of chromosomes during cell division.
- Role of the centromere in spindle fiber attachment
The centromere is the site of attachment for spindle fibers, which are composed of microtubules. These microtubules form the spindle apparatus, which is responsible for moving chromosomes during cell division. The centromere ensures that the chromosomes are properly aligned and segregated during cell division. - Structure of the centromere
The centromere is composed of a complex of proteins that form a specialized structure called the kinetochore. The kinetochore is the site where spindle fibers attach to the centromere. - Importance of the centromere in cell division
The centromere is essential for the accurate segregation of chromosomes during cell division. If the centromere is not properly attached to the spindle fibers, the chromosomes may not be properly separated, which can lead to genetic disorders such as Down syndrome.
The centromere is a critical component of the cell division machinery. It ensures that the chromosomes are properly segregated during cell division, which is essential for the survival and development of organisms.
Kinetochore
The kinetochore is a protein complex that assembles at the centromere of a chromosome and binds to spindle fibers during cell division. It is essential for the accurate segregation of chromosomes during cell division.
The kinetochore serves as the attachment point between the chromosome and the spindle fibers. The spindle fibers are composed of microtubules, which are long, thin protein filaments. The kinetochore ensures that the chromosomes are properly aligned and segregated during cell division.
The kinetochore is a complex structure composed of over 100 different proteins.
- The inner kinetochore is located at the centromere and binds to the centromeric DNA.
- The outer kinetochore projects outward from the inner kinetochore and binds to the spindle fibers.
The kinetochore is essential for the accurate segregation of chromosomes during cell division. If the kinetochore is not properly assembled or attached to the spindle fibers, the chromosomes may not be properly separated, which can lead to genetic disorders such as Down syndrome.
Chromosome condensation
Chromosome condensation is a process that occurs during cell division in which the chromosomes become more compact and condensed. This process is essential for proper chromosome movement and segregation, as it allows the chromosomes to be more easily moved and separated by the spindle apparatus.
The process of chromosome condensation is regulated by a number of proteins, including condensins and topoisomerases. Condensins are proteins that bind to DNA and help to compact it, while topoisomerases are enzymes that help to remove tangles and knots from DNA.
The condensation of chromosomes is essential for accurate cell division. If chromosomes are not properly condensed, they may not be able to be properly separated by the spindle apparatus, which can lead to errors in chromosome segregation. These errors can lead to genetic disorders such as Down syndrome and Klinefelter syndrome.
Connection to "what moves the chromatids around during cell division what organelle anchors these"
The condensation of chromosomes is essential for the proper movement and segregation of chromosomes during cell division. The spindle apparatus, which is responsible for moving the chromosomes, can only attach to condensed chromosomes. If the chromosomes are not properly condensed, they will not be able to be properly attached to the spindle apparatus and will not be able to be moved and segregated properly.
Therefore, chromosome condensation is an essential component of "what moves the chromatids around during cell division what organelle anchors these". Without chromosome condensation, the spindle apparatus would not be able to properly move and segregate the chromosomes, which would lead to errors in cell division and genetic disorders.
FAQs on "what moves the chromatids around during cell division what organelle anchors these"
This section provides answers to frequently asked questions about the movement of chromatids during cell division and the organelles that anchor them.
Question 1: What are chromatids?
Answer: Chromatids are the condensed forms of chromosomes that are visible during cell division. They consist of DNA and proteins.
Question 2: What moves the chromatids during cell division?
Answer: The chromatids are moved by the spindle apparatus, which is a bipolar structure composed of microtubules.
Question 3: What organelle anchors the spindle apparatus?
Answer: The spindle apparatus is anchored by the centrosomes, which are organelles located near the nucleus.
Question 4: What is the importance of accurate chromosome segregation?
Answer: Accurate chromosome segregation is essential for the survival of a cell. If chromosomes are not separated correctly, it can lead to genetic disorders and other problems.
Question 5: What are the consequences of centrosome dysfunction?
Answer: Centrosome dysfunction can lead to a number of problems, including chromosome missegregation, cell division failure, and cancer.
Question 6: How does chromosome condensation contribute to chromatid movement?
Answer: Chromosome condensation is essential for proper chromosome movement and segregation. It allows the chromosomes to be more easily moved and separated by the spindle apparatus.
Summary:
The movement of chromatids during cell division is a complex process that is essential for the survival of a cell. The accurate segregation of chromosomes is ensured by the spindle apparatus, which is anchored by the centrosomes. Chromosome condensation is also essential for proper chromosome movement and segregation.
Next section:
Further exploration of the mechanisms of cell division and their significance in biology.
Tips on Understanding "what moves the chromatids around during cell division what organelle anchors these"
To gain a deeper understanding of "what moves the chromatids around during cell division what organelle anchors these," consider the following tips:
Tip 1: Visualize the process. Draw or find diagrams of cell division and label the different structures involved. This will help you to visualize the process and understand how the chromatids are moved and anchored.
Tip 2: Break down the process into steps. Cell division is a complex process, but it can be broken down into a series of steps. This will make it easier to understand how the different structures work together.
Tip 3: Do some research. There are many resources available online and in libraries that can provide you with more information about cell division. Reading about the topic will help you to understand the concepts in more depth.
Tip 4: Ask questions. If you are struggling to understand something, don't be afraid to ask questions. Your teacher, professor, or a tutor can help you to clarify the concepts.
Tip 5: Practice. The best way to understand cell division is to practice. Work through practice problems and diagrams to test your understanding.
Summary:
By following these tips, you can gain a deeper understanding of "what moves the chromatids around during cell division what organelle anchors these." This knowledge will help you to succeed in your biology studies and to better understand the fundamental processes of life.
Next section:
Conclusion and additional resources for further exploration.
Conclusion
The movement of chromatids during cell division is a complex process that is essential for the survival of a cell. The accurate segregation of chromosomes is ensured by the spindle apparatus, which is anchored by the centrosomes. Chromosome condensation is also essential for proper chromosome movement and segregation.
Understanding the mechanisms of cell division is essential for understanding the fundamental processes of life. This knowledge can be applied to a variety of fields, including medicine, genetics, and evolutionary biology.